Implementing Green Infrastructure for Climate Resilience
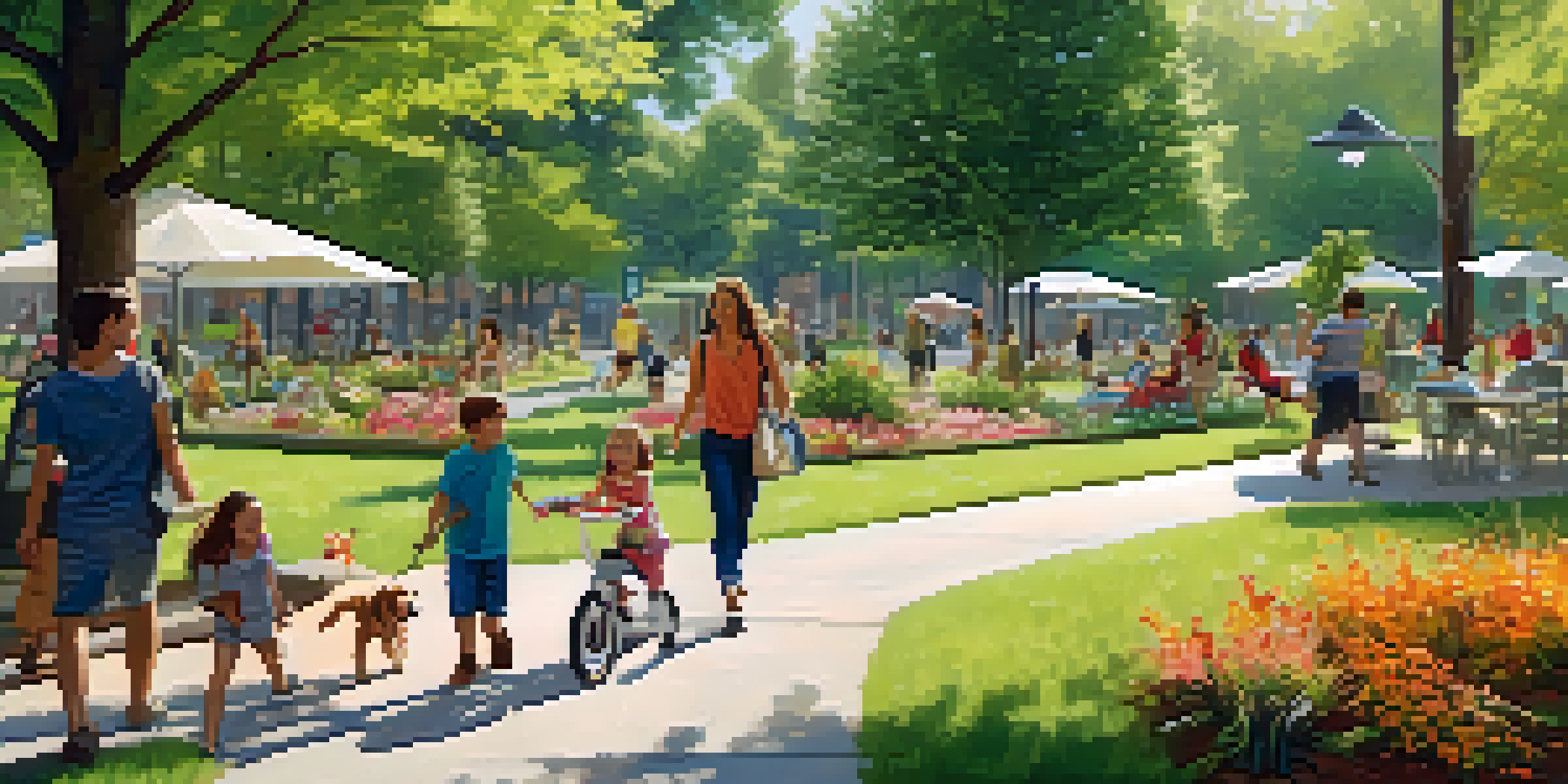
Understanding Green Infrastructure and Its Importance
Green infrastructure refers to a network of natural and semi-natural systems designed to manage stormwater, improve air quality, and enhance biodiversity. Unlike traditional gray infrastructure, which often relies on concrete and pipes, green infrastructure utilizes vegetation, soils, and other elements to achieve environmental benefits. This approach not only helps to mitigate the impacts of climate change but also adds aesthetic value to urban environments.
Green infrastructure is not just about managing water; it’s about creating a better quality of life for all urban residents.
One of the primary reasons for implementing green infrastructure is its ability to enhance climate resilience. As extreme weather events become more frequent due to climate change, cities are increasingly vulnerable to flooding and heatwaves. By integrating green spaces, like parks and green roofs, communities can absorb excess rainwater, reduce urban heat, and promote overall ecological health.
Moreover, green infrastructure contributes to social well-being by creating spaces for recreation and community interaction. It can transform neighborhoods into vibrant areas where residents feel connected to nature and each other, fostering a sense of belonging. This holistic approach emphasizes that environmental health, social equity, and economic vitality are interconnected.
Key Components of Green Infrastructure
There are several essential components of green infrastructure, including green roofs, rain gardens, permeable pavements, and urban forests. Green roofs involve growing vegetation on rooftops, which not only helps insulate buildings but also captures rainwater. Rain gardens are designed to absorb excess rainfall and filter pollutants, making them an effective tool for managing stormwater runoff.
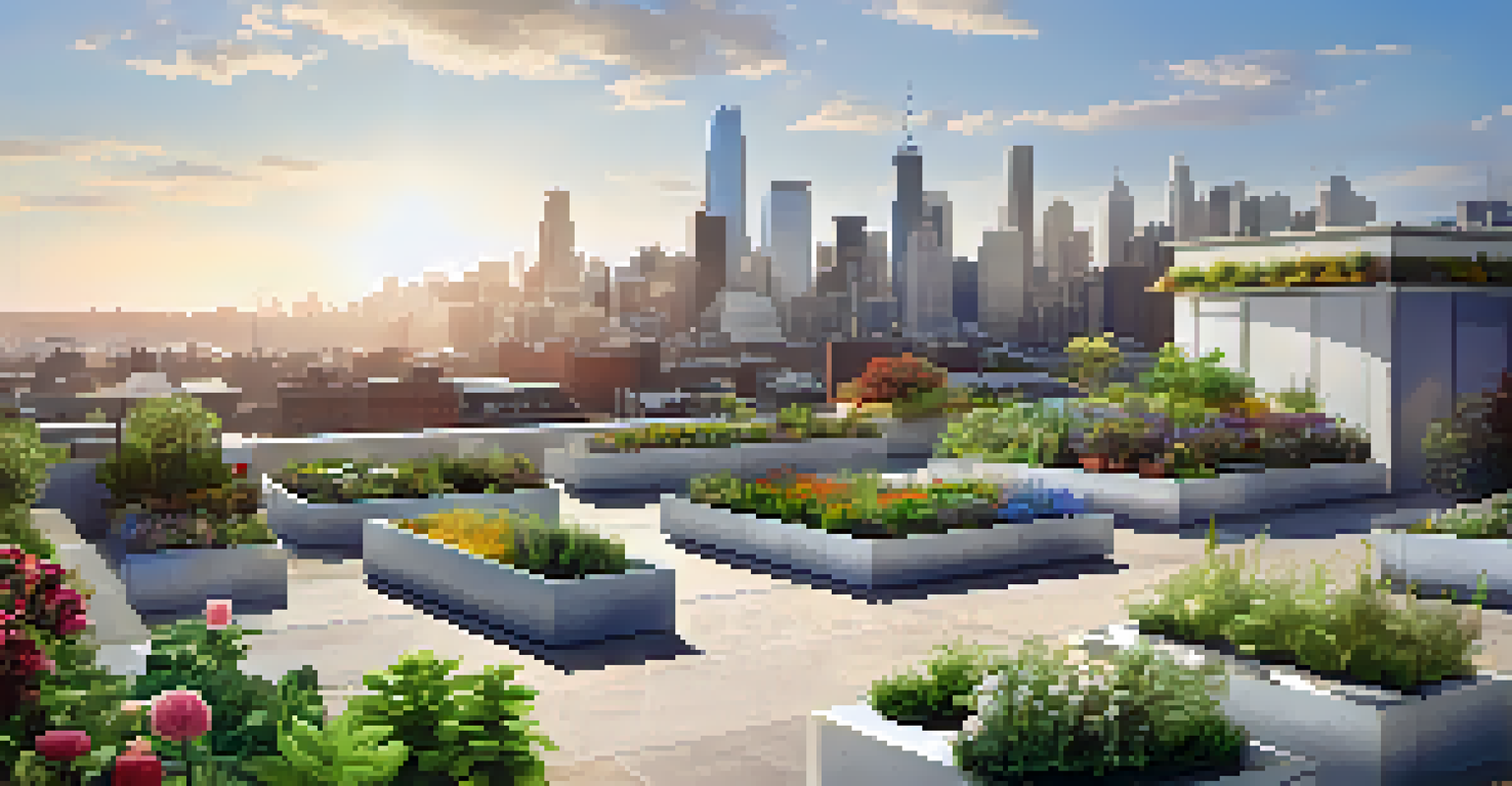

Permeable pavements allow water to seep through the surface, reducing runoff and replenishing groundwater supplies. This innovative solution can be particularly useful in urban areas, where traditional pavement leads to flooding and water quality issues. Urban forests, on the other hand, provide shade, improve air quality, and create habitats for wildlife, making cities more livable.
Green Infrastructure Enhances Resilience
Integrating green spaces helps cities manage stormwater, reduce urban heat, and improve overall ecological health.
Incorporating these elements requires careful planning and design, considering factors like local climate, soil conditions, and community needs. Collaborating with landscape architects, urban planners, and environmental scientists can help ensure that green infrastructure projects are effective and sustainable.
Benefits of Green Infrastructure for Communities
Implementing green infrastructure offers numerous benefits that extend beyond environmental improvements. For instance, it can significantly reduce urban heat islands, making cities more comfortable during hot weather. By increasing green spaces, communities can also improve air quality, which is crucial for public health, particularly in densely populated areas.
The future will not be about the built environment versus nature; it will be about how we integrate the two.
Moreover, green infrastructure can enhance local economies by attracting businesses and tourism. Areas with parks and greenery are often more desirable places to live, leading to increased property values. This economic uplift can create jobs in landscaping, maintenance, and ecological restoration, benefiting the community as a whole.
Additionally, green infrastructure promotes biodiversity by providing habitats for various species. This not only contributes to ecological balance but also allows residents to experience nature within their urban environments, fostering a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
Challenges in Implementing Green Infrastructure
While the benefits of green infrastructure are compelling, there are challenges in its implementation. One major hurdle is funding; many cities operate on tight budgets and may struggle to prioritize green initiatives. Securing grants, leveraging public-private partnerships, and engaging community stakeholders can help overcome this financial barrier.
Another challenge lies in the maintenance of green infrastructure systems. Unlike traditional infrastructure, green elements require ongoing care and investment to thrive. This includes regular watering, weeding, and monitoring for pests, which can be resource-intensive for municipalities.
Community Engagement is Key
Involving residents in the planning and maintenance of green infrastructure fosters support and strengthens community bonds.
Furthermore, there may be resistance from community members who are unfamiliar with the concept of green infrastructure. Education and outreach efforts are essential to inform residents about the benefits and importance of these systems, ensuring community buy-in and support for future projects.
Case Studies of Successful Green Infrastructure Projects
Several cities around the world have successfully implemented green infrastructure projects that serve as excellent models. For example, New York City’s Green Infrastructure Program focuses on creating green roofs, rain gardens, and bioswales to manage stormwater runoff. This initiative has not only reduced flooding but also improved the city’s quality of life by adding green spaces.
In Philadelphia, the Green City, Clean Waters program has transformed the urban landscape by investing in green streets, parklets, and other green infrastructure elements. This project aims to reduce the city’s reliance on traditional stormwater systems, demonstrating that a greener approach can yield significant environmental and social benefits.
These case studies illustrate that with the right strategies and community involvement, green infrastructure can be a viable solution for urban challenges. They provide valuable lessons for cities looking to enhance their climate resilience and create sustainable environments.
Engaging Communities in Green Infrastructure Initiatives
Community engagement is crucial for the success of green infrastructure projects. When residents are involved in the planning and design stages, they are more likely to support and maintain these initiatives. Organizing workshops, focus groups, and community meetings can help gather input and foster a sense of ownership among residents.
Education plays a key role in engaging communities. By raising awareness of the benefits of green infrastructure, cities can inspire residents to take an active role in its implementation. This can include volunteer opportunities for planting trees, maintaining community gardens, or participating in local clean-up events, which not only improve the environment but also strengthen community bonds.
Economic Benefits of Green Spaces
Green infrastructure not only improves environmental quality but also boosts local economies by increasing property values and attracting tourism.
Additionally, collaborating with local schools and organizations can create educational programs that teach the next generation about sustainability and environmental stewardship. By instilling these values early on, communities can build a culture that prioritizes green infrastructure and climate resilience for years to come.
The Future of Green Infrastructure and Climate Resilience
As cities face the realities of climate change, the future of green infrastructure looks promising. With increasing awareness and advocacy for sustainable practices, more municipalities are prioritizing green solutions in their urban planning. This shift reflects a growing understanding that environmental health is essential for overall community well-being.
Advancements in technology are also enhancing the effectiveness of green infrastructure. Innovations such as smart irrigation systems and data analytics can help optimize the maintenance and performance of green elements. This tech-driven approach ensures that cities can maximize their investments in green infrastructure while adapting to changing climate conditions.

Ultimately, the successful implementation of green infrastructure will depend on collaboration across various sectors, including government, private organizations, and communities. By working together, we can create resilient urban landscapes that not only withstand climate challenges but also thrive in harmony with nature.